Which of the Following Best Describes the Proton Motive Force
An electrochemical gradient formed by protons outside the cell membrane. A chemical gradient represent as PH gradient from protons.
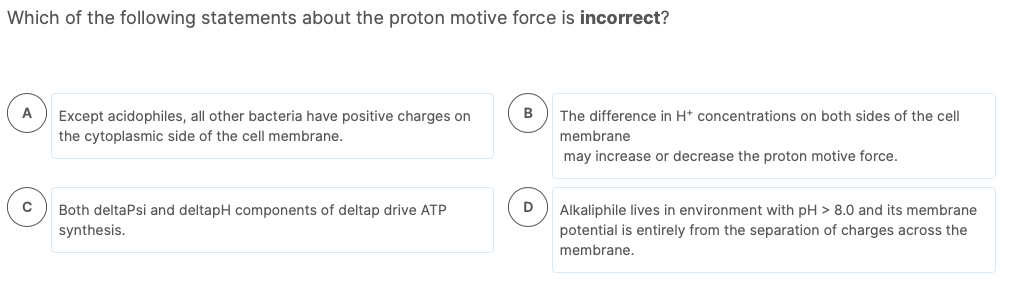
Solved Which Of The Following Statements About The Proton Chegg Com
Describe subunit a in F0 component.
. The proton-motive force created by the pumping out of protons by the respiratory chain complexes is in the mitochondria of most tissues mainly used to translocate protons through the ATP synthase complex leading to the formation of. Which of the following best describes the proton motive force in the chloroplast in the mitochondria together. An essential property of all bacterial cells.
Chemical gradient delta H charge gradient delta Ψ Note. Proton motive force Delta P. Which phrase best describes the proton-motive force.
These complexes are made up of the e carriers mentioned earlier the exact combination and number of which differ between organisms. B generate the substrates ADP and Pi for the ATP synthase. See Page 1.
Charge gradient- distribution of electric charges creates an electrical voltage. C induce a conformational change in the ATP synthase. The proton motive force has two possible beginnings.
Which of the following best describes the proton motive force. ATP synthase is the enzyme complEx that harnesses proton-motive force to. Mitochondria use a proton motive force but chloroplasts do not need to because of the electron transport chain.
Facilitated gated Facilitated channel Active. View the full answer. A create a pore in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What can prevent electron. Up to 10 cash back Proton motive force PMF is the force that promotes movement of protons across membranes downhill the electrochemical potential. ATP is generated by proton motive force created by.
A proton motive force is An energized state across a membrane resulting from a proton gradient An energized state across a membrane resulting from an electron gradient. What does the proton-motive force cause in terms of the active sites. All bacteria require a proton motive force pmf to grow and remain viable under replicating and non-replicating conditions.
Membrane potential and the gradient of proton concentration. The force needed to move protons into the inner mitochondrial spacec. During respiration energy is conserved by the generation of a pmf across a proton-impermeable membrane.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Overview A difference of solute concentration between two compartments separated by a biological membrane generates a tendency to equilibrium which in the case of protons is called proton motive force PMF. A the diffusion of water down an electrochemical gradient that drives ATP synthesis B a proton gradient that drives redox reactions of electron transport C a proton-motive force that activates ATP synthase to produce ATP D an ATP synthase that pumps protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane using ATP as an energy source E the uptake.
The proton motive force across the inner mitochondrial membrane has two components. A Potential energy from ATP b Protons powering the electron transport system c Formation. The proton gradient is built in the intermembrane space in mitochondria and in the intermembrane space in chloroplasts.
Chemical gradient- a concentration gradient of protons establishes pH differences across membrane. Regulation of metabolic pathways includes regulation of an enzyme in a pathway by increasing or decreasing its response to signals. The proton motive force is made as an example of what type of molecular movement.
This inhibition prevents oxidative phosphorylation by inhibiting the formation of the proton-motive force. 4H move to the outside of. D oxidize NADH to NAD.
E reduce O2 to H2O. One way the proton motive force begins is with the donation of H from NADH to flavin mononucleotide FMN to make FMNH 2. During oxidative phosphorylation the proton motive force that is generated by electron transport is used to.
-it causes them to sequentially change functions as protons flow through the membrane-embedded component of the enzyme We can think of ATP synthase as consisting of a moving part and a stationary part. One half channel opens to the intermembrane space and the other to the matrix. Control involves monitoring the effects that these changes in an.
Subunit a which abuts the c ring has two channels that reach halfway into the a subunit. The free energy associated with the removal of hydrogen from NADH d. The proton-motive force is aATP synthase.
The respiratory chain and ATP synthase are biochemically separate systems linked only by a proton motive force. 21 Generation of the proton motive force. The combination of a proton and voltage gradient across the membrane ANS.
Cthe proton concentration gradient. The amount of energy required to protonate a glucose molecule b. Dthe movement of electrons across the membrane.

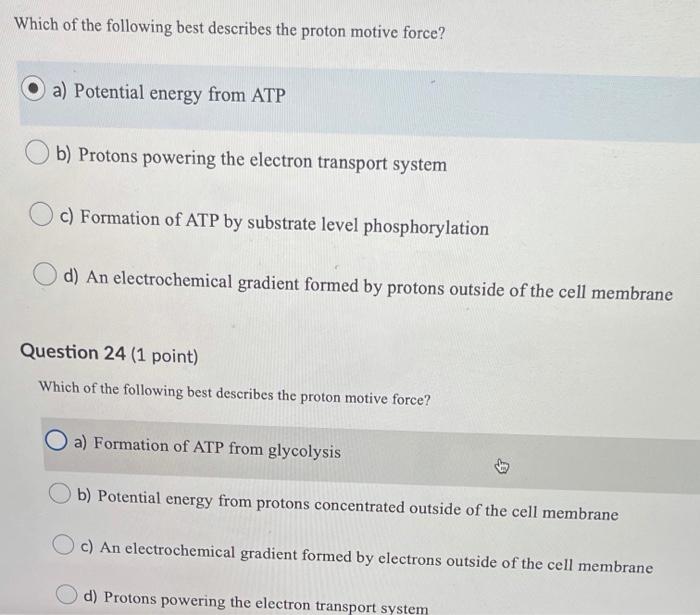
Solved Which Of The Following Best Describes The Proton Chegg Com
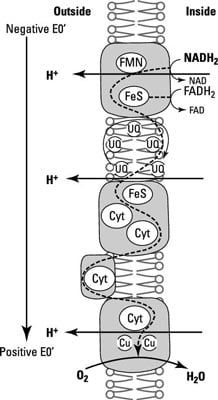
The Proton Motive Force Dummies

Solved Which Of The Following Is The Best Description Of A Proton Motive Force A Situation In Which One Side Of A Membrane Has A Greater Concentration Of Ht Ions Than The Other

Schematic Diagram Of The Mechanism Of Proton Motive Force Generation By Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment